Logger in SpringBoot
Hello geeks, here I came up with another interesting blog on Logger in java spring boot. To understand the logger we need their requirement first.
In our application there are some situations, where our code breaks or behaves abnormally, to understand this we need some of the trace of code. Mean from where and why this abnormal or code break happens. So, we need to track or print out the class name, method name with line number from where the issue occurred.
So, all in all we just need a console out put mentioning the exact issue with class level and method level details with line number. We, can use a simple system.out.println but it has no any flexibility and configuration on application level, Like filtering the log level, filtering the packaging etc.
The logging facilities are there on JDK since 1.0 under java.utils.logging packag in Logger class. We get the hold of this static class's object using Logger.getLogger(ClassName).
Log level
- Info- - for info messages
- Severe -- for severe messages
- Fine -- for fine debugged message
Handlers
- File Handler -- logging into file
- Console Handler -- logging to console
Issue with JSK 1.0 Logging
- Performance Issues
- Not flexible
- Needed More Features
So, we need a framework or plugin for proper control and configuration of logging. Some of the popular logging frame works are LOG4J, SLF4J, Logback and LOG4J2.
Log4j is one of the earlier frameworks in java for logging. In same fashion we can get hold of Logger class. and different logging levels are-
- logger.debug()
- logger.error()
- logger.info()
- File log handler
- Console log handler
- Rolling File (Daily) log handler
- JDBC log handler
- SMTP log handler
- JMS log handler
- Formatting Options
The same time when LOG4J is becoming popular among developers there are other logging frameworks are introducing into the market and they are not compatible to each other.
So people moving towards People move towards facade libraries like:-
- SLF4J
- APACHE COMMONS
To over come this issue SLF4J was introduced, which is actually consists of interfaces mentioning the standards of logging, and other logging frameworks implements those standards to make things in action. SLF4J is that much popular that other logging frameworks came up with their own standards similar to SLF4J, but they didn't got popularity.
Today's two popular logging frameworks are
- Logback
- Log4J2
Both framework are successor of LOG4J.
Logback is the recommended way since, it is developed by the same guy who develop the LOG4J and SLF4J.
LOG4J2 has it's own features like -
- Lazyloading
- Asyn logging
Logging level priority
Trace < Debug < Info < Warn < Error < Fatal.
Our spring boot application is already came up with logger dependency added to it if it has spring-boot-starter-web dependency, which implicitly added dependency of spring-boot-starter-logging which is dependent on spring-jcl (spring common logging bridge) for logging stuff.
We can get hold of Logger by below code snippet.
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ScheduledTasks.class);
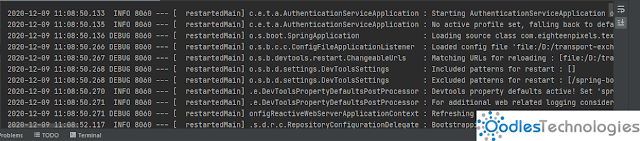
The default log message format is as follows:-
- Date and Time – Millisecond precision and easily sortable.
- Log Level – ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG or TRACE.
- Process ID.
- A “—” separator to distinguish the start of actual log messages.
- Thread – Enclosed in square brackets (may be truncated for console output).
- Logger – This is usually the source class name (often abbreviated).
- The log message.'
- FATAL, ERROR -- Red
- WARN --Yello--
- INFO, DEBUG, TRACE -- Green
You can filter the logs based on packages filter and level either using application properties or yml file.
logging.level.root=WARN
logging.level.my.package=DEBUG
logging.file = main.log
logging.path = log
That's all about logging in spring boot, hope you guys feel this blog informative. Thanks.


Comments
Post a Comment