Spring boot security basics
Hello geeks, here i came up with another blog series on spring security, Where I am going to explore some of the basic concepts behind the spring boot security as well as hands on examples.
This is going to be the first blog in this series on spring boot security, so please follow all blogs in order to better understanding of the concepts.
Before we begin to deep dive into spring security, we need to under stand why we need application level security. Since we have already OS level security, server level security then why we need this application level security. The answer is pretty much self explanatory, since we are developing APIs in java, these end points are explicitly exposed to end user that's why all the already applied security on OS level and server are forcefully by passed here.
So, all in all we need another application level security here. For this spring security came to the rescue here.
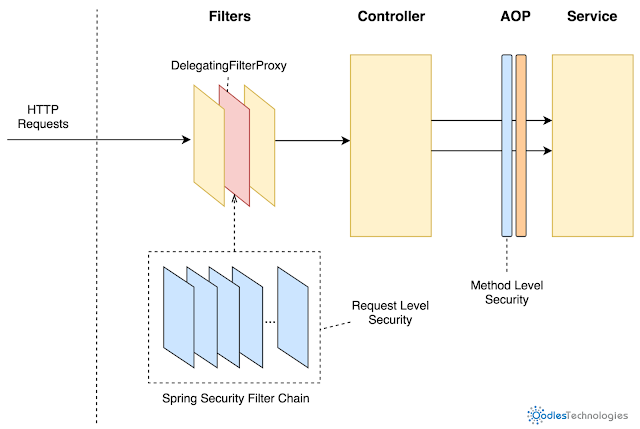
In real spring security is a filters standing between your application and all the incoming request coming to the application server. It verifies each and every request made to server and validates it, is it authenticated and authorized to access the requested end point on the basis of some pre defined authorized and authentication rules.
So, Spring security is an application frame work which provides:
- Login and logout functionality.
- Allow/block access to URLs to users.
- Allow/block access to URLs to logged in users and with certain roles(access control).
It handles a lots of vulnerabilities on it's own with providing any extra configurations, like Session fixations, click jacking, click site and request forgery.
Types of authentication can be achieved using spring boot are as follows:-
- Username/password base authentication
- SSO/Okta/LDAP (Single sign on authorization)
- App level authorization
- Intra App authorization using OAuth
- Micro-Service security
- Method level security
5 core concepts in spring-security
- Authentication: It is a way to uniquely identifies the requesting user by tany one of the following methods:-
* Knowledge based authentication by providing user name/password or pin or question ( like pet name etc.) that are actually provided by end user at the time of registration.
* Possession base authentication is some thing like only you are at the possession of providing that information like OTP, access card etc, that only you can have this.
* Multi factor authentication is the combination of both above knowledge base and possession based authentication to make sign in more secure. - Authorization: It is a boolean check that confirms that is requested user is eligible to perform requested operation or not.
- Principal: It is the environment or preferences a user has configured to his account, you can things principal as current logged in user. where he has configured things according to his preferences, this may be different for different user account.
- Granted Authority: It is a list of authorized activities to a particular user account. Like a user can view his balance, language preferences, transactions history. But he is not allowed to delete a particular transaction history.
- Role: It is the granted authority, or you can say it is a collection of granted authority based on certain position like admin has approx all granted authority present into the system but a user has not. So admin and users are two different role here.
That's all required core concepts to dive into spring security, in the next blog I will implement a sample spring boot service using spring security.
Hope you enjoyed this blog and find this useful.



Comments
Post a Comment